Phone owning
This article will show you how to get started in performing penetration testing on cell phones to see if it can be compromised by accessing their data via Bluetooth (BT). This is an important part of penetration testing as many bad things can be done to someone’s phone without their knowledge. If they own your Phone, they own your life.
This is an advanced article so you need the following base knowledge: You need to be able to boot a Backtrack 4r2 disk on a compute that has Bluetooth device installed. You can use other distros if you like but BackTrack has 32 tools just for Bluetooth.
Bluetooth was designed as a serial port replacement. Just like serial ports of old, you need to set an IRQ and a Memory address to interact with other devices. Bluetooth needs a Channel and Memory addresses set to interact with other phones.
Let’s Start
With Backtrack booted up to the command line and the Bluetooth adapter installed type: hciconfig you should see all the “acceptable” devices. If no device appears on the list and you have
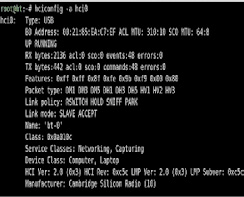
the device plugged in, well, your device won’t work. Sorry, you need to try a different device. Not all BT adapters are created equal. If a device appears (hci0) then bring it up: hciconfig hci0 up, just like it was a wireless card. The hciconfig –a command should return a list of features for all the Bluetooth adapters on the computer. It should look like this:
Let’s pretend we’re a phone
Notice in the above example that our Service / Device Class shows we’re a computer. Notice the Link mode is SLAVE ACCEPT. We want to change all of this so we look like another cell phone. Type this at the command prompt:
hciconfig -a hci0 class 0x500204
hciconfig -a hci0 lm accept, master;
hciconfig -a hci0 lp rswitch,hold,sniff,park;
hciconfig -a hci0 auth enable
hciconfig -a hci0 encrypt enable
hciconfig -a hci0 name Resume
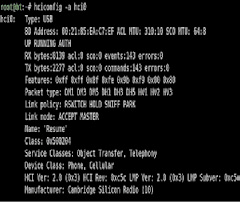
Now run hciconfig –a again and notice the differences.
The last command to change the name is important because that’s what appears on the screen. Would you take a call from “bt-0” or “Resume” or “ “? Notice what the Service / Device Class is now. You’re a Phone!
Who else is out there?
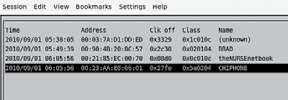
There are several good tools for scanning on Backtrack, l2ping (that’s an L not the number 1), hcitool scan, sdptools browse and this one BTscanner.
What we’re after is the Address of the device, think MAC address of a network card and the cannel each service is offered on. When you click on a device it gives you more information, specifically the cannel of each service offered and memory addresses of the device.
What Now?
Let’s start with a simple program that does lots. My favorite is bluebugger because you can change Option parameters quickly till it works properly. Notice the different modes that bluebugger offers.
You can do it all from the command line: ~#./bluebugger –m Ron –c 7 –a xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx dial 1900badpeople . Lets look at this command, simply add the channel and connection name (here it’s a blank, I use Resume). Seems to simple yes? Very true, it doesn’t work on every phone that has the Bluetooth on so you need to try lots of different.
I look at a lot of Phones and some brands are easier to penetrate than others. Which ones? Depends on model, make and how it’s setup. With so many Bluetooth tools here are a few all purpose basic tools to learn: Hciconfig, Bluescan, l2Ping, SDPTool, hcitool, BTScanner, Bluesnarfer, Bluebugger, Carwhisper.
Bluetooth devices are growing number daily. Security is poor at best, coupled with the predicted increase in mobile threats, and NOW is the time to secure yours and your businesses Bluetooth devices.
Here’s help!
NIST “Guide to Bluetooth Security” 800-121
www.Backtrack-Linux.org
www.soldierx.com/bbs/201001/Bluetooth-hacking-wth-Backtrack-4
www.trifinite.org
About the Author:
Brad Smith started breaking his toys at a very early age. When he wrote his first computer buffer overload in 1972 which totally wrecked the University computer system, he realized the potential to break much larger things. Now he spends his time teaching other to break small things that have large importance, like cell phones.