Digital Forensics Concepts Part2
In Part1, we discussed some concepts regarding the cyber crime, digital forensics and Digital Forensics Evidence, and now we will present the practical process to investigate Cyber Crimes.
Link of Part 1 | http://www.bluekaizen.org/digital-investigation-concepts-part1/
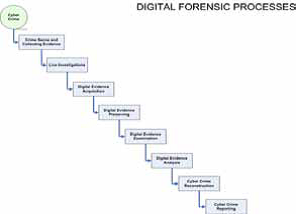
Cyber Crime investigating Process
Whenever we have a cyber-crime there should be consistent digital forensics process to define the expected results of the investigation. Going through each step in the digital forensics process and studying the expected output will the investigation to reach admissible finding.
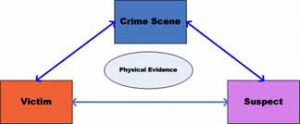
- A crime scene is a location where an illegal act took place and there could be more than one crime scene, sometimes there is a primary crime scene and secondary and tertiary crime scene. One of the main goals in an investigation is to attribute the crime to its perpetrator by uncovering compelling links between the offender, victim, and crime scene.
According to Locard’s Exchange Principle, anyone, or anything, entering a crime scene takes something of the scene with them, and leaves something of the behind when they leave.
Electronic evidence is an information and data of investigative value that is stored on, processed or transmitted by an electronic
device. Any data may be exist in three major status for example a computer running operating system data may be stored in hard disk or may be in memory for the purpose of processing or sending it to over network or internet and you can collect evidences in every status and if we back to the diagram in figure 3 based on many factor you can decide from which status you can collect you evidence.
There are some types of Fragile Evidence
- Transient data – Information that will be lost at shutdown, such as open network connections, memory resident programs, etc.
- Timely Fragile data – Data that is stored on the hard disk, but can easily be altered, such as last accessed time stamps.
- Temporarily accessible data – Data that is stored on the disk, but for a period of time only
- Live Investigation is one of the most important steps especially in case of hacking investigation and sometimes you would collect some live information from
the victim even before you shutdown the system to collect. Doing live investigation may reduce your investigation time and will direct you to the right investigation plan.
And we are expecting to have all process running, network connection, image physical memory running application, opened documents, and other as output form live investigation steps
- Digital evidence acquision is the process of acquiring any digital device and taking a bitstream copy of it and bitstream copy meaning exact image of the digital image on physical layer level and the objective is to create a forensically image that you can start working with it for the next phase of you analysis without doing any damage for your original digital evidence
- Digital evidence preserving is the phase of how to keep you evidences in safe from collecting phase till reporting phase and there are a lot of standards of how to keep the integrity of you digital evidences through certain process and procedures including the technical integrity checks required in any movement of the digital evidences
- Digital examination is the phase of removing any anti forensics technics exist in your digital evidence like compressed, encryption, hidden, misnamed, password protection, steganography, and all other
anti-forensics technics that may be make the forensics analysis hard. And in this phase there are some technics may be used like filter/reduction, class/Individual characteristics, data recovery / salvage
- Digital Evidence analysis leads to a more complete picture of a crime that will be done through live information analysis, file system analysis, log file analysis, registry analysis, internet traces, mail investigation and other based on cyber crime types.
- Cyber Crime reconstruction is the phase that you are trying to identify what happened exactly based on timeline plan and collect all the evidence that prove your conclusion. What happened, who caused the events when, where, how, and why functional analysis, relational analysis, and temporal analysis. Example of relational analysis as shown to identify relationships between suspect, Victim, and Crime Scene It will be useful to create nodes representing places, e-mail, IP addresses used, Telephone number.
- Cyber crime report
is the most important part which conclude all the finding point with some condition that help others to decide if our cyber crime report is admissible or not and it describes how the data has been acquired during the collection and reporting phases.
Report is the final product that will be provided to the department that requested the digital investigative support from your team. It is important that the report only describe facts that were observed, analyzed, and thus documented. The report should be a neutral and detached observation on the information that was observed during the analysis. If you put information subjectivity into the report, you are no longer being an objective reporter. The most important role that a digital investigator and a digital investigative and/or electronic discovery facility can bring to the enterprise is neutrality in capture, analysis, and reporting.
About The Author
Mounir Kamal
(Section Manager – Incident Handling and Digital Forensics),
CISA, Crangie Mellon CERT/CC Certified Incident Handler, CEH, CHFI, CREA